Shopping Cart
- Remove All
 Your shopping cart is currently empty
Your shopping cart is currently empty

Neogambogic acid, an active ingredient in garcinia, can inhibit the growth of some solid tumors [resulting in an anticancer effect], and may be responsible for the inhibition of proliferation of human breast cancer cell line MCF-7 cells.
| Pack Size | Price | Availability | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 mg | $46 | In Stock | |
| 5 mg | $98 | In Stock | |
| 10 mg | $148 | In Stock | |
| 25 mg | $249 | In Stock | |
| 50 mg | $369 | In Stock | |
| 100 mg | $548 | In Stock |
| Description | Neogambogic acid, an active ingredient in garcinia, can inhibit the growth of some solid tumors [resulting in an anticancer effect], and may be responsible for the inhibition of proliferation of human breast cancer cell line MCF-7 cells. |
| In vitro | Neo-gambogic acid(NGA) significantly reduced the proliferation of MCF-7 cells in a dose-dependent manner. NGA could increase the expression of the apoptosis-related proteins FasL, caspase-3, caspase-8, caspase-9, and Bax and decrease the expression of anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 accompanied by the mitochondrial transmembrane damage. The antiproliferative effect of NGA on MCF-7 cells is due to the G(0)/G(1) arrest, increased apoptosis and activation of Fas/FasL and cytochrome C pathway[1]. |
| In vivo | Neo-gambogic acid(NGA) dose of ≤0.4 μg/ml had no significant effect on the proliferation of mouse BMMs in vitro (P>0.05);?concentrations of between 0.1-0.4 μg/ml significantly inhibited RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis (P<0.01) in a dose-dependent manner.?Compared with the control group, NGA significantly reduced RANKL-induced bone resorption in vitro (P <0.01), and downregulated the expression of osteoclast-related mRNAs of TRAP, CTR, CTSK, and NFATc1.?NGA suppressed the activation of JNK but not the p38 signaling pathway and significantly reduced NF-κB p65 phosphorylation and the nuclear transport of NF-κB molecules, which inhibited NFATc1 expression.?CONCLUSIONS NGA suppressed RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis by inhibiting the JNK and NF-κB pathways in mouse BMMs in vitro and reduced osteoclastic bone resorption[2]. |
| Cell Research | MCF-7 cells (5* 10^4 ) were seeded into 96-well plates.Four hours later, 10 ul NGA in DMSO was added into the wells at various concentrations (0.5-24 ug/ml) and 0.1% DMSO was set as a negative control.?After 72 h, 50 ul MTT was added and cells were incubated for another 4 h. Then, media was removed and 150 ul DMSO was added and the plates were placed on a shaking table at 150 rpm for 10 min. Optical density (OD) was measured at 490 nm.?The experiment was repeated thrice and the rate of cell inhibition was calculated using the following formula: inhibition rate [1-(OD test/ OD negative control)]*100%[1]. |
| Animal Research | Primary mouse BMMs were cultured with increasing concentrations of NGA.?Real-time polymerase chain reaction was used to study the expression of mRNAs corresponding to gene products specific to receptor activator of NF-κB ligand (RANKL)-induced osteoclast differentiation, including tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP), calcitonin receptor (CTR), cathepsin K (CTSK), and nuclear factor of activated T cells c1 (NFATc1).?A cell counting kit-8 assay was used to evaluate cell proliferation.?Western blotting and confocal immunofluorescence microscopy were used to investigate the signaling pathways.?A bone resorption model was used to quantify bone resorption[2]. |
| Alias | neo-gambogic acid |
| Molecular Weight | 646.77 |
| Formula | C38H46O9 |
| Cas No. | 93772-31-7 |
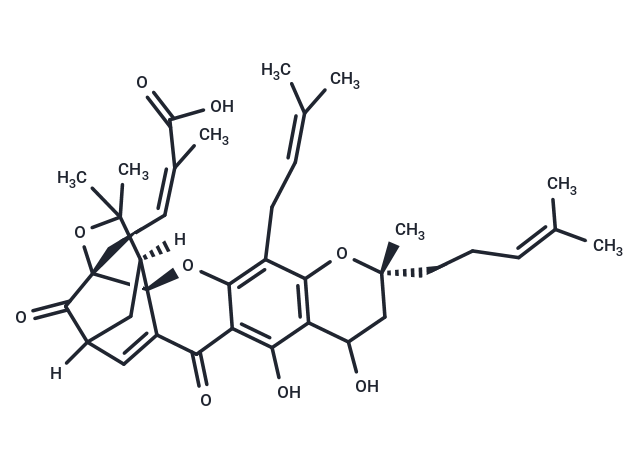
| Smiles | C(/C=C(\C(O)=O)/C)[C@@]12[C@]34C(C(=O)C=5C(O3)=C(CC=C(C)C)C6=C(C5O)C(O)C[C@](CCC=C(C)C)(C)O6)=CC(C1=O)(C[C@]4(C(C)(C)O2)[H])[H] |
| Relative Density. | 1.32 g/cm3 |
| Storage | keep away from direct sunlight | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Solubility Information | DMSO: 6.47 mg/mL (10 mM), Sonication is recommended. | ||||||||||||||||||||
Solution Preparation Table | |||||||||||||||||||||
DMSO
| |||||||||||||||||||||

Copyright © 2015-2025 TargetMol Chemicals Inc. All Rights Reserved.